2021 – Earthquake T-wave propagation from the Pacific Kermadec Trench to the Atlantic Ocean
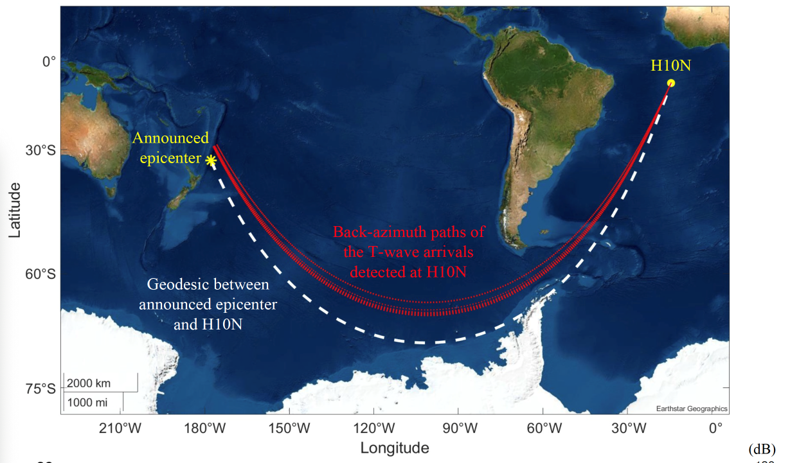
Kermadec Trench earthquake epicenter and the geodesic path (dashed white line) to the CTBT IMS H10N array (Ascension Island). Red lines present the back-azimuth geopaths of the T-wave arrivals detected at H10N.
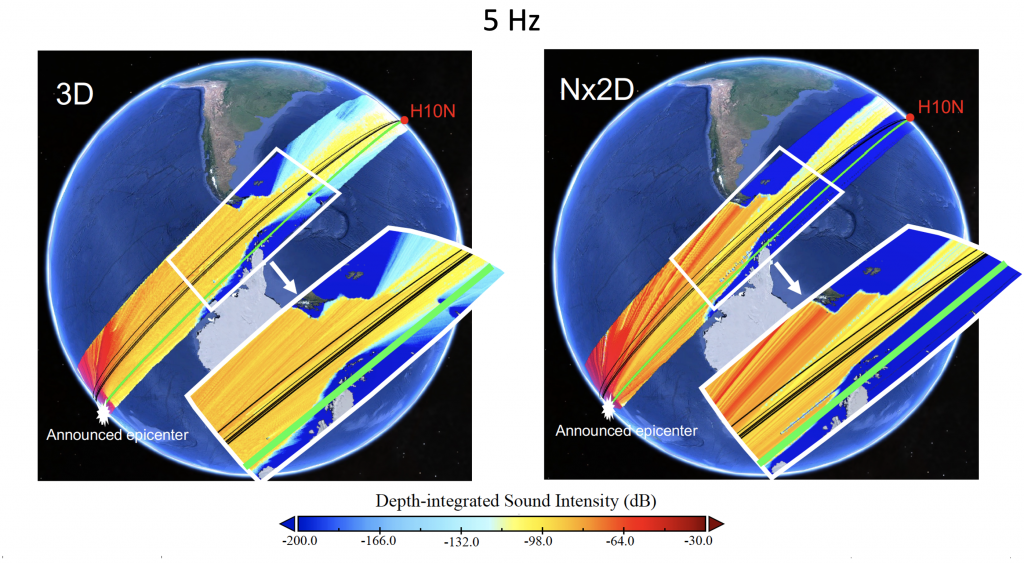
Comparison of 2d vs 3d propagation modeling from T-wave source
On 18 June 2020, an Mw7.4 submarine earthquake occurred in the Kermadec Trench, northeast of New Zealand. This powerful earthquake triggered energetic tertiary waves (T-waves) that propagated through the South Pacific Ocean into the South Atlantic Ocean, where the T-waves recorded by a hydrophone station near Ascension Island 15,127 km away from the epicenter. A three-dimensional PE sound propagation model was used to investigate the discrepancy betwen the T-wave ageo-path and the back-azimuth propagated paths. (JASA Express Lett. 1, 126001 (2021); https://doi.org/10.1121/10.0008939)