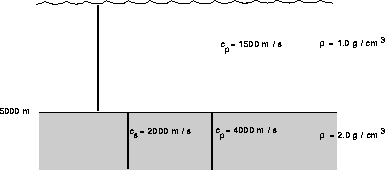
Figure: Schematic of the SCHOLTE problem.

Figure: Schematic of the SCHOLTE problem.
This problem is a version of the Pekeris waveguide but with an elastic half-space as the bottom. This type of problem has a Scholte mode with a phase velocity less than the slowest speed in the problem. (Since the source and receiver are many wavelenghts from the interface the Scholte mode is not actually important for the transmission loss calculation.)
'Scholte waveguide' 10.0 1 'NVM' 500 0.0 5000.0 0.0 1500.0 / 5000.0 1500.0 / 'A' 0.0 5000.0 4000.0 2000.0 2.0 / 1400.0 2000.0 1000.0 ! RMAX (km) 1 500.0 / ! NSD SD(1:NSD) 1 2500.0 / ! NRD RD(1:NRD)
KRAKEN- Scholte waveguide
Frequency = 10.00 NMEDIA = 1
N2-LINEAR approximation to SSP
Attenuation units: dB/m
VACUUM
Z ALPHAR BETAR RHO ALPHAI BETAI
( Number of pts = 500 RMS roughness = 0.000E+00 )
0.00 1500.00 0.00 1.00 0.0000 0.0000
5000.00 1500.00 0.00 1.00 0.0000 0.0000
( RMS roughness = 0.000E+00 )
ACOUSTO-ELASTIC half-space
5000.00 4000.00 2000.00 2.00 0.0000 0.0000
CLOW = 1400.0 CHIGH = 2000.0
RMAX = 1000.000000000000
Number of sources = 1
500.0000
Number of receivers = 1
2500.000
Mesh multiplier CPU seconds
1 5.61
2 6.51
4 4.64
I K ALPHA PHASE SPEED
1 0.4400982929E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1427.677728
2 0.4188306870E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1500.173101
3 0.4186856672E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1500.692715
4 0.4184439022E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1501.559773
5 0.4181052921E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1502.775838
6 0.4176696933E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1504.343123
7 0.4171369148E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1506.264510
8 0.4165067147E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1508.543581
9 0.4157787955E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1511.184643
10 0.4149527997E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1514.192774
11 0.4140283053E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1517.573853
12 0.4130048217E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1521.334613
13 0.4118817854E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1525.482682
14 0.4106585562E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1530.026639
15 0.4093344142E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1534.976071
16 0.4079085559E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1540.341632
17 0.4063800914E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1546.135118
18 0.4047480418E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1552.369538
19 0.4030113364E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1559.059197
20 0.4011688100E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1566.219793
21 0.3992192010E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1573.868514
22 0.3971611492E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1582.024153
23 0.3949931943E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1590.707232
24 0.3927137754E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1599.940135
25 0.3903212305E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1609.747258
26 0.3878137986E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1620.155170
27 0.3851896232E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1631.192776
28 0.3824467597E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1642.891500
29 0.3795831866E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1655.285463
30 0.3765968244E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1668.411654
31 0.3734855636E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1682.310086
32 0.3702473075E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1697.023903
33 0.3668800348E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1712.599409
34 0.3633818906E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1729.085975
35 0.3597513167E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1746.535736
36 0.3559872314E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1765.002998
37 0.3520892659E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1784.543272
38 0.3480580404E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1805.211941
39 0.3438954040E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1827.062890
40 0.3396044231E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1850.148255
41 0.3351886824E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1874.521915
42 0.3306503451E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1900.250643
43 0.3259872074E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1927.433091
44 0.3211925126E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1956.205410
45 0.3162787575E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1986.597316
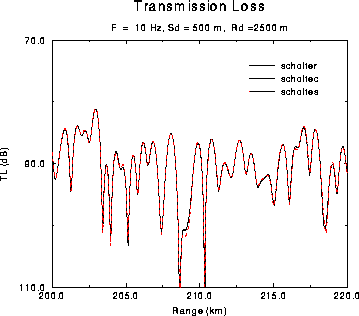
Figure: Transmission loss for the SCHOLTE problem.