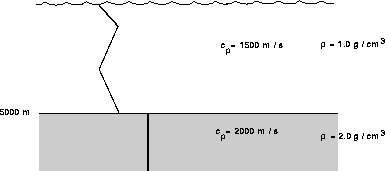
Figure: Schematic of the DOUBLE problem.

Figure: Schematic of the DOUBLE problem.
The ocean profile is converted to one involving three piecewise linear segments defining a double-duct profile.
'Double-duct problem'
10.0
3
'NVF'
100 0.0 1000.0
0.0 1500.0 /
1000.0 1550.0 /
200 0.0 3000.0
1000.0 1550.0 /
3000.0 1500.0 /
200 0.0 5000.0
3000.0 1500.0 /
5000.0 1550.0 /
'A' 0.0
5000.0 2000.0 0.0 2.0 0.0 0.0
1400.0 2000.0
1000.0 ! RMAX (km)
1 500.0 / ! NSD SD(1:NSD)
1 2500.0 / ! NRD RD(1:NRD)
KRAKEN- Double-duct problem
Frequency = 10.00 NMEDIA = 3
N2-LINEAR approximation to SSP
Attenuation units: dB/mkHz
VACUUM
Z ALPHAR BETAR RHO ALPHAI BETAI
( Number of pts = 100 RMS roughness = 0.000E+00 )
0.00 1500.00 0.00 1.00 0.0000 0.0000
1000.00 1550.00 0.00 1.00 0.0000 0.0000
( Number of pts = 200 RMS roughness = 0.000E+00 )
1000.00 1550.00 0.00 1.00 0.0000 0.0000
3000.00 1500.00 0.00 1.00 0.0000 0.0000
( Number of pts = 200 RMS roughness = 0.000E+00 )
3000.00 1500.00 0.00 1.00 0.0000 0.0000
5000.00 1550.00 0.00 1.00 0.0000 0.0000
( RMS roughness = 0.000E+00 )
ACOUSTO-ELASTIC half-space
5000.00 2000.00 0.00 2.00 0.0000 0.0000
CLOW = 1400.0 CHIGH = 2000.0
RMAX = 1000.000000000000
Number of sources = 1
500.0000
Number of receivers = 1
2500.000
Mesh multiplier CPU seconds
1 5.60
2 6.18
I K ALPHA PHASE SPEED
1 0.4171018652E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1506.391084
2 0.4147891740E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1514.790091
3 0.4131862874E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1520.666464
4 0.4123681174E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1523.683583
5 0.4117017415E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1526.149801
6 0.4104029641E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1530.979515
7 0.4091561041E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1535.645013
8 0.4080128302E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1539.947973
9 0.4074949725E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1541.904988
10 0.4068324597E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1544.415928
11 0.4057281144E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1548.619650
12 0.4046123964E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1552.889967
13 0.4035440690E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1557.001029
14 0.4024224926E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1561.340487
15 0.4011172669E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1566.421051
16 0.3996592323E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1572.135660
17 0.3980769235E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1578.384713
18 0.3964207800E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1584.978796
19 0.3946677171E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1592.019067
20 0.3927946746E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1599.610614
21 0.3907987820E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1607.780166
22 0.3886748929E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1616.565778
23 0.3864545686E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1625.853546
24 0.3841222010E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1635.725634
25 0.3816711818E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1646.229951
26 0.3790948500E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1657.417743
27 0.3763853318E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1669.349142
28 0.3735627690E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1681.962398
29 0.3706135033E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1695.347107
30 0.3675356291E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1709.544548
31 0.3643204686E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1724.631430
32 0.3609604877E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1740.685067
33 0.3574683553E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1757.689937
34 0.3538311960E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1775.757869
35 0.3500480248E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1794.949511
36 0.3461083089E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1815.381239
37 0.3420046728E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1837.163585
38 0.3377442369E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1860.338274
39 0.3333144286E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1885.062502
40 0.3287145204E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1911.441362
41 0.3239342265E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1939.648482
42 0.3189739326E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1969.811532
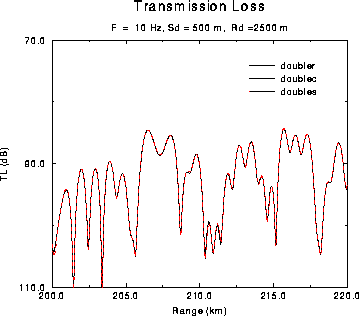
Figure: Transmission loss for the DOUBLE problem.