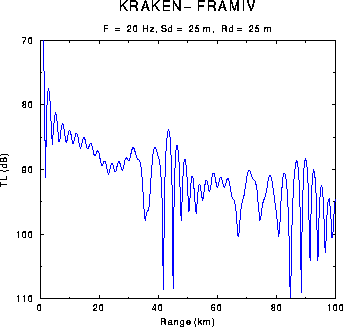
Figure: Sample output of PLOTTLR: transmission loss vs. range for the Arctic problem.
PLOTTLR sums the modes to produces plots of coherent transmission loss versus range.
Files:
Name Unit Description
Input
*.PLP 1 PLot Parameters
*.MOD 30-99 MODe files
Output
*.PRT 6 PRinT file
---------------------------------------------------------
EXAMPLE AND DESCRIPTION OF PLP FILE:
'RAN' ! OPT (cart, cylin or scaled coords)
999 ! M (number of modes to include)
1, 0.0 ! NPROF RPROF(1:NPROF) (km)
25.0 25.0 ! SD RD (m)
0.0 100.0 501 10.0 10.0 ! RMIN RMAX NR RINC (km) RAXL (cm)
70.0 110.0 10.0 6.0 ! TLMIN TLMAX TLINC (dB) TLAXL (cm)
0.0 ! 3dB smoothing window (m)
(1) - OPTIONS
Syntax:
OPTION
Description:
OPTION(1:1): Source type.
'R' point source.
(cylindrical or R-Z coordinates)
'X' line source.
(cartesian or X-Z coordinates)
OPTION(2:2): Selects coupled mode or adiabatic mode theory
'C' for Coupled mode theory.
'A' for Adiabatic mode theory (default).
For a coupled mode run you ***must*** be sure that the
modes are finely sampled throughout the water column
so that FIELD can accurately
calculate the coupling integrals. This is done by using
a large number of receiver depths (NRD) when you
do the KRAKEN run. This number should be set to
give about 10 points/wavelength.
OPTION(3:3): Component
'' (null) for pressure.
'H' for Horizontal displacement.
'V' for Vertical displacement.
'T' for Tangential stress.
'N' for Normal stress.
(2) - NUMBER OF MODES
Syntax:
M
Description:
M: Number of modes to use in the field computation.
If this number is larger than the actual number of
modes in the mode file it is reduced accordingly.
(3) - PROFILE RANGES
Syntax:
NPROF RPROF(1:NPROF)
Description:
NPROF: The number of profiles, i.e. ranges where a new
set of modes is to be used.
RPROF(): Ranges (km) of each of these profiles.
For a range independent problem there is only
one profile and its range is arbitrary. Mode
files must exist for each range of a new
profile and be assigned in sequence to units
30,31,... The modes for the last SSP profile
are extended in a range-independent fashion to
infinity so that RMAX can exceed RPROF(NPROF).
(4) - SOURCE/RECEIVER DEPTHS
Syntax:
SD RD
Description:
SD: Source depth (m).
RD: Receiver depth (m).
(5) - RECEIVER RANGES/AXIS INFO
Syntax:
RMIN RMAX NR RINC RAXL
Description:
RMIN: First receiver range (km).
RD: Last receiver range (km).
NR: Number of receiver ranges.
RINC: Range interval for tick marks (km).
RAXL: Range axis length (cm).
(6) - TRANSMISSION LOSS AXIS INFO
Syntax:
TLMIN TLMAX TLINC TLAXL
Description:
TLMIN: TL minimum (dB).
TLMAX: TL maximum (dB).
TLINC: TL interval for tick marks (dB).
TLAXL: TL axis length (cm).
If you set TLMIN=TLMAX then the curve is autoscaled.
(7) - SMOOTHING WINDOW
Syntax:
DR3DB
Description:
DR3DB: Three dB smoothing window (m).
The tranmission loss is computed then smoothed in
range using a Gaussian filter. DR3DB gives the
range interval over which the smoothing is
performed.

Figure: Sample output of PLOTTLR: transmission loss vs. range for the
Arctic problem.