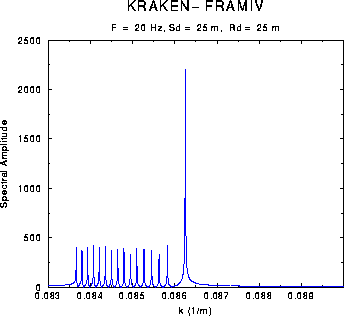
Figure: Sample output of PLOTGRN: the Green's function for the Arctic problem.
PLOTGRN uses the modes to produces plots of the amplitude of the Green's function, G(k) corresponding to a particular source/receiver combination. The Green's function is plotted as a function of horizontal wavenumber, k.
Files:
Name Unit Description
Input
*.PLP 1 PLot Parameters
*.MOD 30 MODe file
Output
*.PRT 6 PRinT file
---------------------------------------------------------
EXAMPLE AND DESCRIPTION OF PLP FILE:
25.0 25.0, ! SD RD (m)
2000 2.5E-6, ! NKPTS ATTEN (attenuation)
0.083 0.090 0.001 15.0 ! KMIN, KMAX, KINC, KAXL (cm)
0.0 2400.0 600.0 9.0 ! GMIN, GMAX, GINC, GAXL (cm)
(1) - SOURCE/RECEIVER DEPTHS
Syntax:
SD RD
Description:
SD: Source depth (m).
RD: Receiver depth (m).
(2) - SAMPLING INFORMATION
Syntax:
NKPTS
ALPHA
Description:
NKPTS: Number of points in k-space for evaluating
the kernel.
ALPHA: Stabilizing attenuation (1/m).
Since G(k) has singularities on the real k-axis, it is
evaluated on a slice displaced into the complex plane a
distance i ALPHA.
(3) - AXIS INFO
Syntax:
KMIN KMAX KINC KAXL
GMIN GMAX GINC GAXL
Description:
KMIN: k-minimum (1/m).
KMAX: k-maximum (1/m).
KINC: k-interval for tick marks (1/m).
KAXL: k-axis length ( cm).
GMIN: G-minimum.
GMAX: G-maximum.
GINC: G-interval for tick marks.
GAXL: G-axis length ( cm).
If GMAX is set to zero, the program will automatically
compute a value.

Figure: Sample output of PLOTGRN: the Green's function for the
Arctic problem.