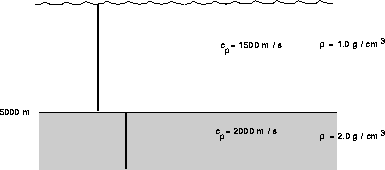
Figure: Schematic of the PEKERIS problem.

Figure: Schematic of the PEKERIS problem.
This problem involves a homogeneous fluid layer with a sound speed of
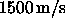 overlying a faster bottom with sound speed
overlying a faster bottom with sound speed 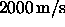 and density of
and density of 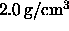 .
.
'Pekeris problem'
10.0
1
'NVF'
500 0.0 5000.0
0.0 1500.0 /
5000.0 1500.0 /
'A' 0.0
5000.0 2000.0 0.0 2.0 /
1400.0 2000.0
1000.0 ! RMAX (km)
1 500.0 / ! NSD SD(1:NSD)
1 2500.0 / ! NRD RD(1:NRD)
KRAKEN- Pekeris problem
Frequency = 10.00 NMEDIA = 1
N2-LINEAR approximation to SSP
Attenuation units: dB/mkHz
VACUUM
Z ALPHAR BETAR RHO ALPHAI BETAI
( Number of pts = 500 RMS roughness = 0.000E+00 )
0.00 1500.00 0.00 1.00 0.0000 0.0000
5000.00 1500.00 0.00 1.00 0.0000 0.0000
( RMS roughness = 0.000E+00 )
ACOUSTO-ELASTIC half-space
5000.00 2000.00 0.00 2.00 0.0000 0.0000
CLOW = 1400.0 CHIGH = 2000.0
RMAX = 1000.000000000000
Number of sources = 1
500.0000
Number of receivers = 1
2500.000
Mesh multiplier CPU seconds
1 5.49
2 6.21
I K ALPHA PHASE SPEED
1 0.4188332253E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1500.164010
2 0.4186958032E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1500.656385
3 0.4184666447E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1501.478167
4 0.4181455674E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1502.631092
5 0.4177323161E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1504.117605
6 0.4172265636E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1505.940862
7 0.4166279103E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1508.104751
8 0.4159358848E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1510.613904
9 0.4151499439E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1513.473722
10 0.4142694720E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1516.690399
11 0.4132937809E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1520.270954
12 0.4122221089E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1524.223270
13 0.4110536194E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1528.556132
14 0.4097873993E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1533.279285
15 0.4084224568E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1538.403485
16 0.4069577186E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1543.940567
17 0.4053920272E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1549.903522
18 0.4037241363E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1556.306582
19 0.4019527072E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1563.165317
20 0.4000763035E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1570.496741
21 0.3980933859E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1578.319442
22 0.3960023053E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1586.653720
23 0.3938012967E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1595.521741
24 0.3914884708E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1604.947725
25 0.3890618058E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1614.958141
26 0.3865191380E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1625.581942
27 0.3838581509E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1636.850824
28 0.3810763645E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1648.799530
29 0.3781711221E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1661.466183
30 0.3751395766E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1674.892680
31 0.3719786754E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1689.125136
32 0.3686851438E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1704.214399
33 0.3652554677E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1720.216633
34 0.3616858743E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1737.194000
35 0.3579723130E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1755.215440
36 0.3541104368E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1774.357560
37 0.3500955866E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1794.705659
38 0.3459227830E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1816.354868
39 0.3415867360E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1839.411384
40 0.3370818983E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1863.993688
41 0.3324026217E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1890.233379
42 0.3275436107E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1918.274423
43 0.3225014368E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1948.265834
44 0.3172824619E-01 0.0000000000E+00 1980.312832
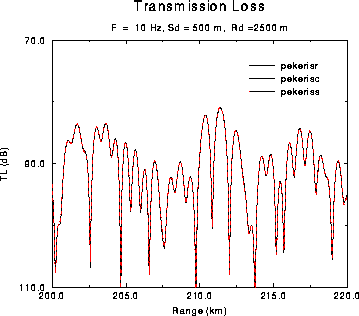
Figure: Transmission loss for the PEKERIS problem.